The GameBoyTM
is a portable device with simple operation. The user interface
comprises four buttons, a joypad, integrated four color gray scale
screen and a speaker. Stereo sound is available from the headphone
jack. The internal hardware includes a Z80 processor derivative
together with system RAM and ROM.
These
features make the GameBoyTM ideal for menu
controlled applications. Programming a a home telephone system for
example would be much easier using the GameBoyTM
LCD and joypad than using the telephone pad.
The following table provides more detailed technical information on the hardware inside the GameBoyTM
|
|
8-bit Z80-like CPU running at 4.194304MHz |
|
|
8-bit data-BUS, 16-bit address-BUS |
|
|
8kB internal can be extended to up to 32kB external |
|
|
8kB internal |
|
|
16kBit, 32kBit, 64kBit, 128kBit,... up to 4MBit cartridges are known. |
|
|
4 channels. Each of which can be mapped either to the left or to the right or to both speakers. |
|
|
Display: Reflective LCD 160x144 dots
(physically) |
|
|
One serial port. Up to 4 GameBoyTM can be connected together using these ports. Baud rate and protocol are not fully documented. |
|
|
Classic: 6 Volts, 0.7 Watts, 4 AA Batteries
- 35 hours |
Further information can be found in "gbspec.txt“. Titled "Everything You Always Wanted To Know About GameBoyTM but were afraid to ask“. It is one of the best sources of information for both hardware and software including useful algorithims and common problems/pitfalls.
Figure 1: General hardware schematic
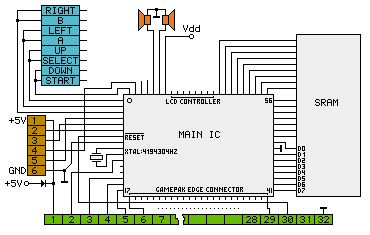 Figure 1 shows a schematic of the GameBoyTM
internal hardware. Starting from the left, there are
the buttons and joypad, the serial port, an oscillator, the speakers,
the CPU and the main memory. On the lower side the connector to the
cartridge is shown. For further information on the GameBoyTM
internal hardware and logic use
this schematic (Figure
2) drawn by Jeff
Frohwein.
Figure 1 shows a schematic of the GameBoyTM
internal hardware. Starting from the left, there are
the buttons and joypad, the serial port, an oscillator, the speakers,
the CPU and the main memory. On the lower side the connector to the
cartridge is shown. For further information on the GameBoyTM
internal hardware and logic use
this schematic (Figure
2) drawn by Jeff
Frohwein.